http://fwd5.wistia.com/medias/28h51kfcir?embedType=iframe&videoFoam=true&videoWidth=640
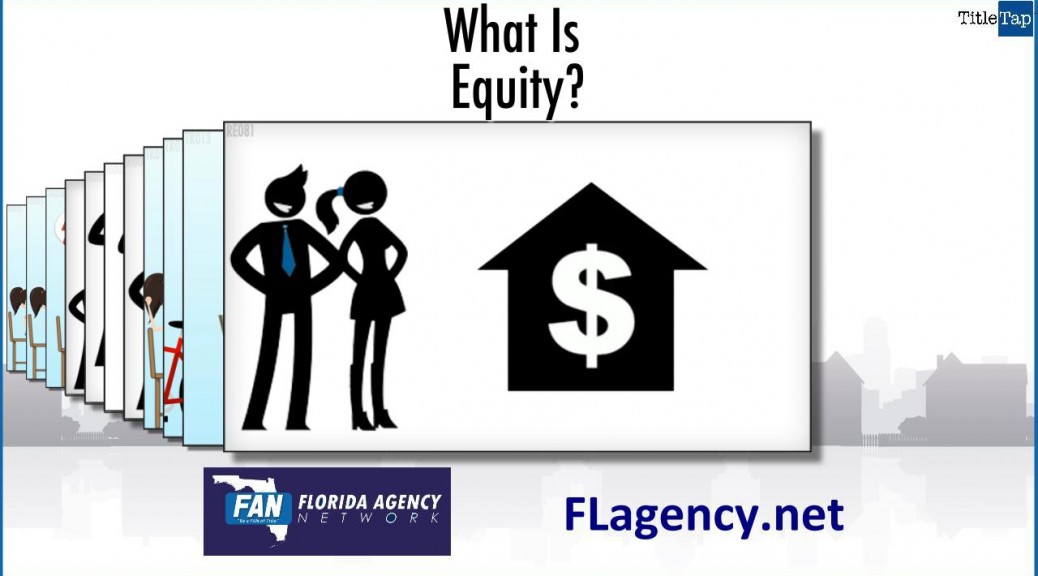
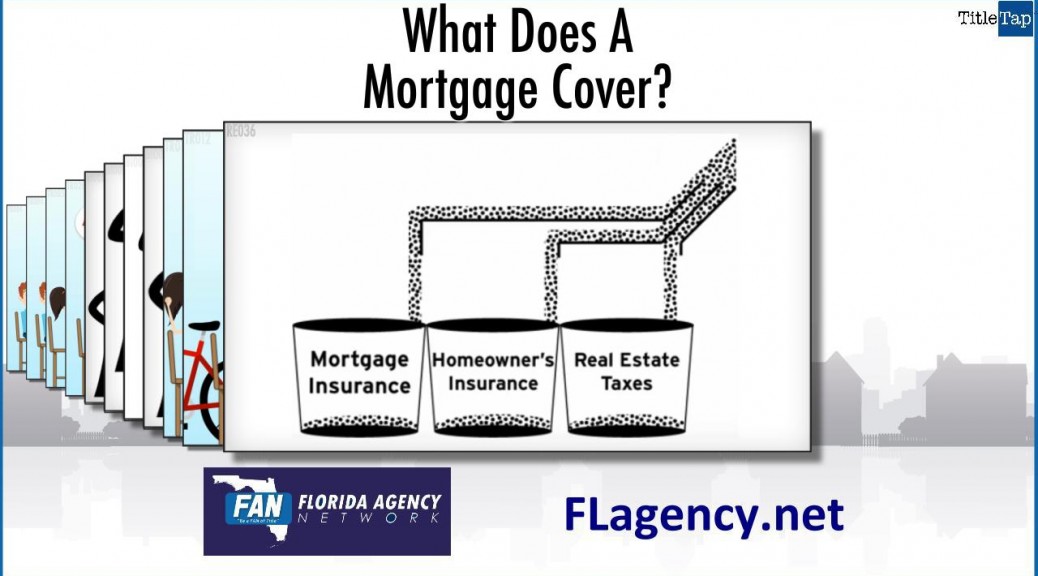
Equity is the value YOU own in property such as a house. It’s the difference between what’s OWED and what the property is WORTH in the current market.
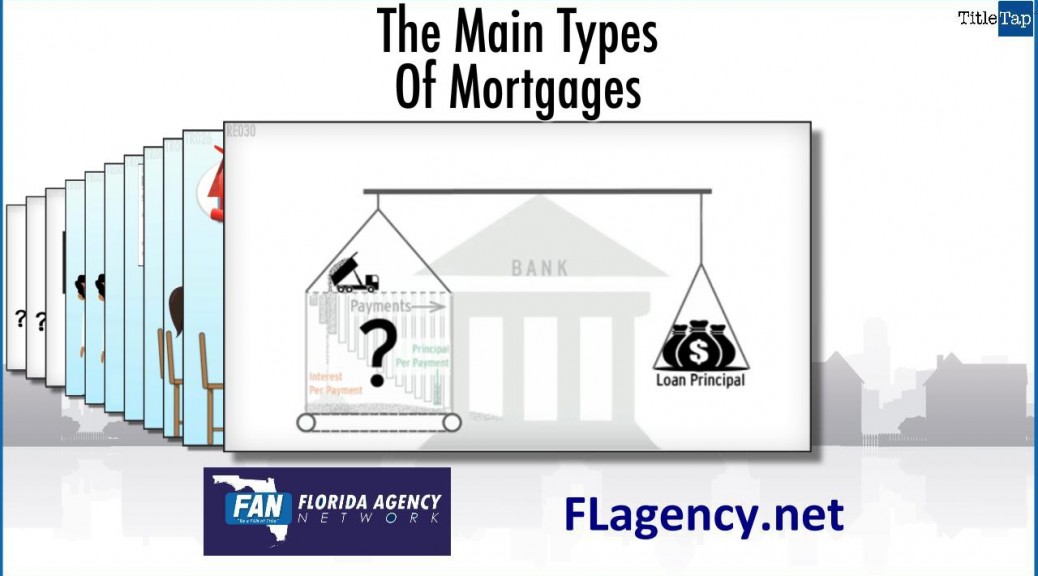
The example this video shows – you have a house worth $300,000 today and you owe the bank $200,000. Your equity would be $100,000.
If the house is valued at $500,000 in five years, and you still owe $150,000 your equity will be $350,000.
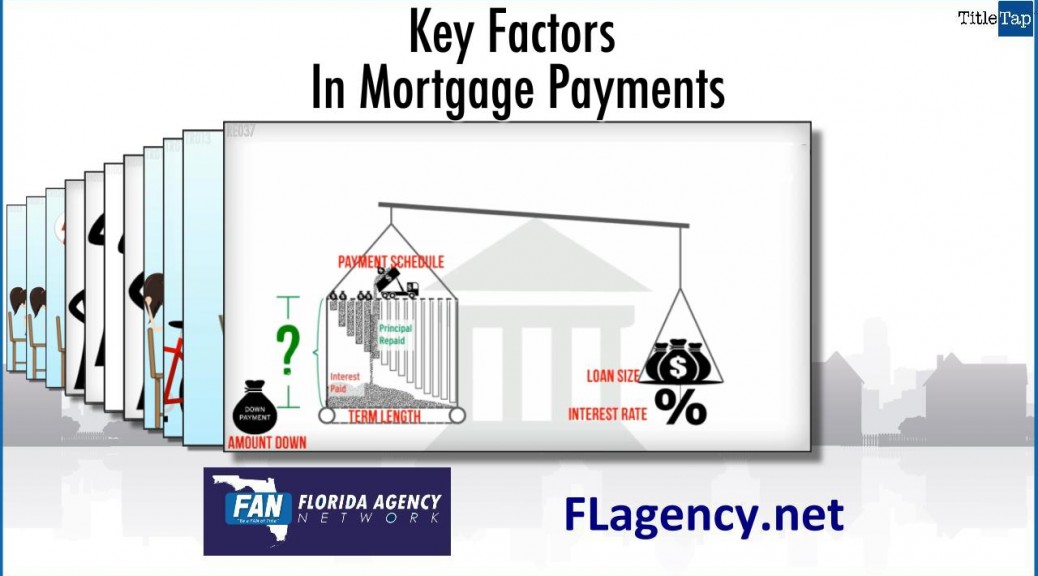
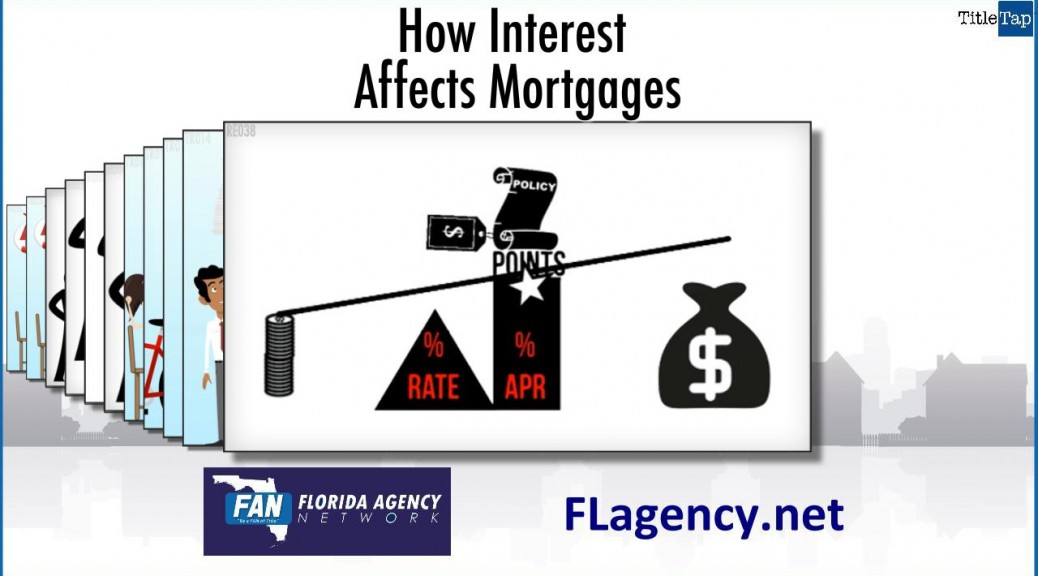
Equity grows if the property value goes up or if the amount owed goes down. The key thing to remember, simple as it sounds, is that you “own” increases in value. The bank’s loan doesn’t go up if the home’s value goes up.
Equity in a home can be used as collateral for loans but a house is not a piggy bank. Home equity can become a key financial asset over time; treat it wisely.