http://fwd5.wistia.com/medias/bwes79dhza?embedType=iframe&videoFoam=true&videoWidth=640
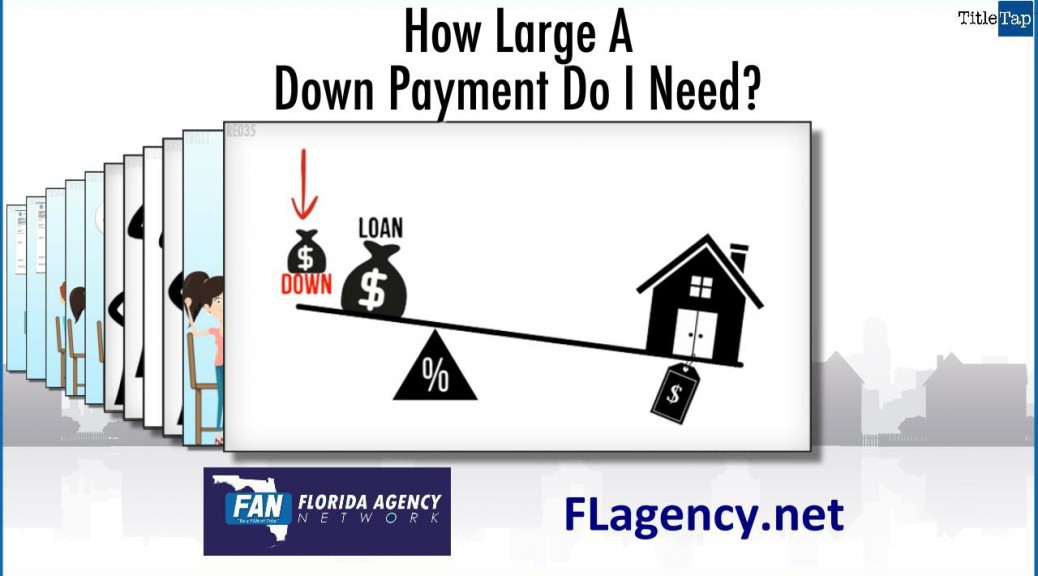
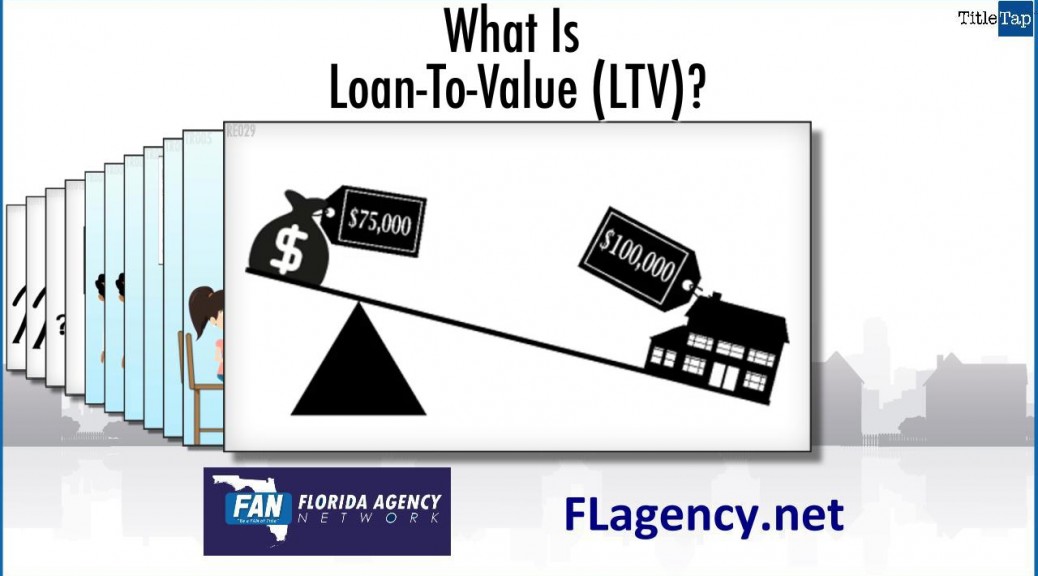
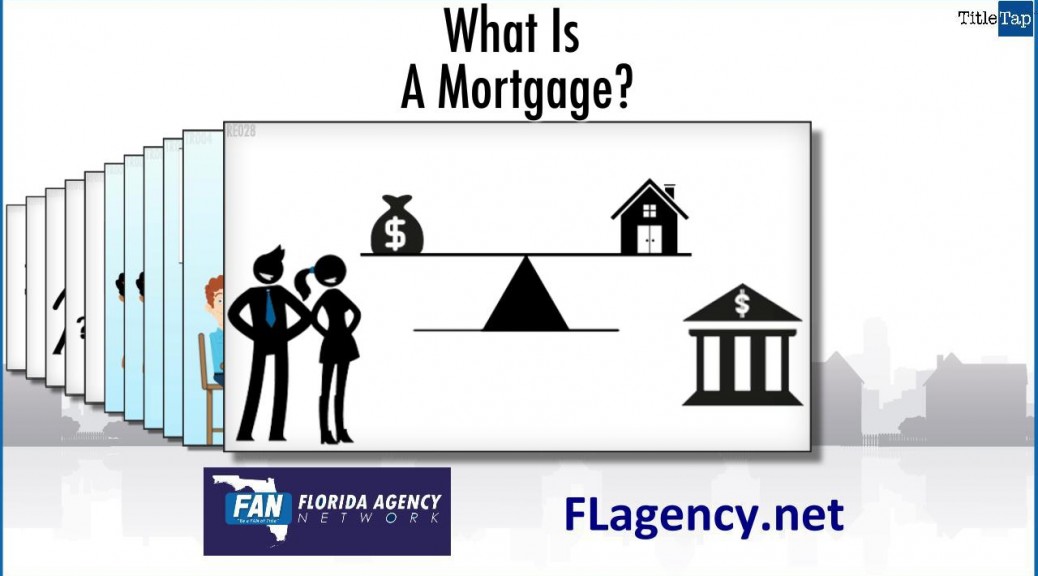
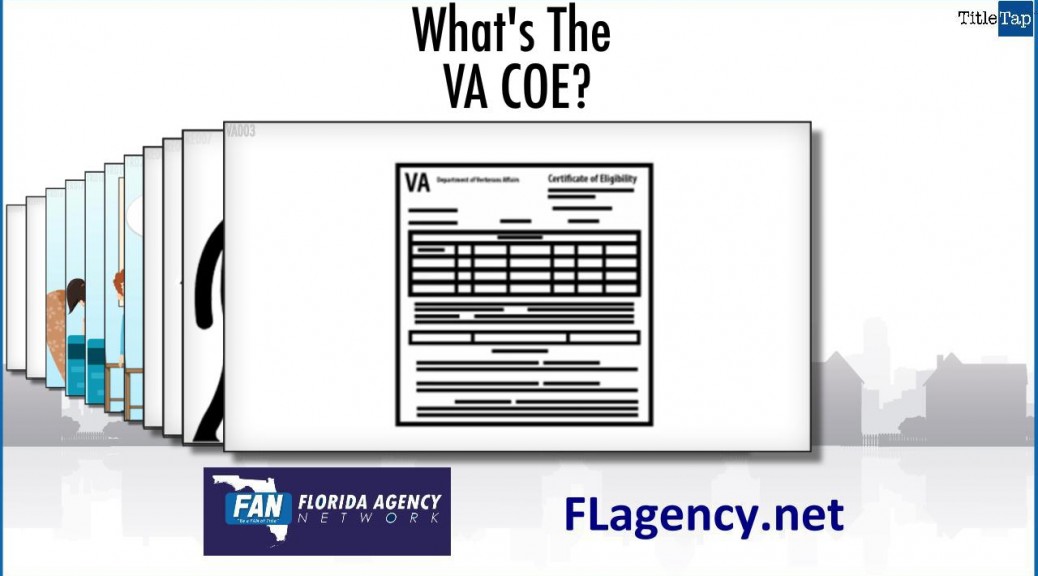
Yes. Like the video shows, lenders now offer several affordable mortgage options which can help first-time homebuyers overcome obstacles that made purchasing a home difficult in the past.
Lenders may now be able to help borrowers who don’t have a lot of money saved for the down payment and closing costs, have no or a poor credit history, have quite a bit of long-term debt, or who have experienced income irregularities.