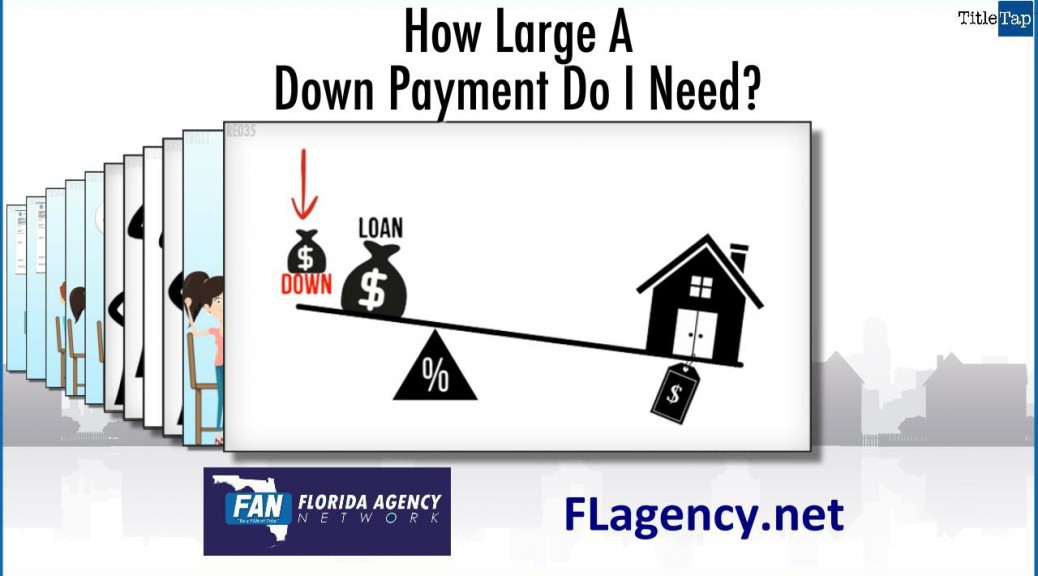
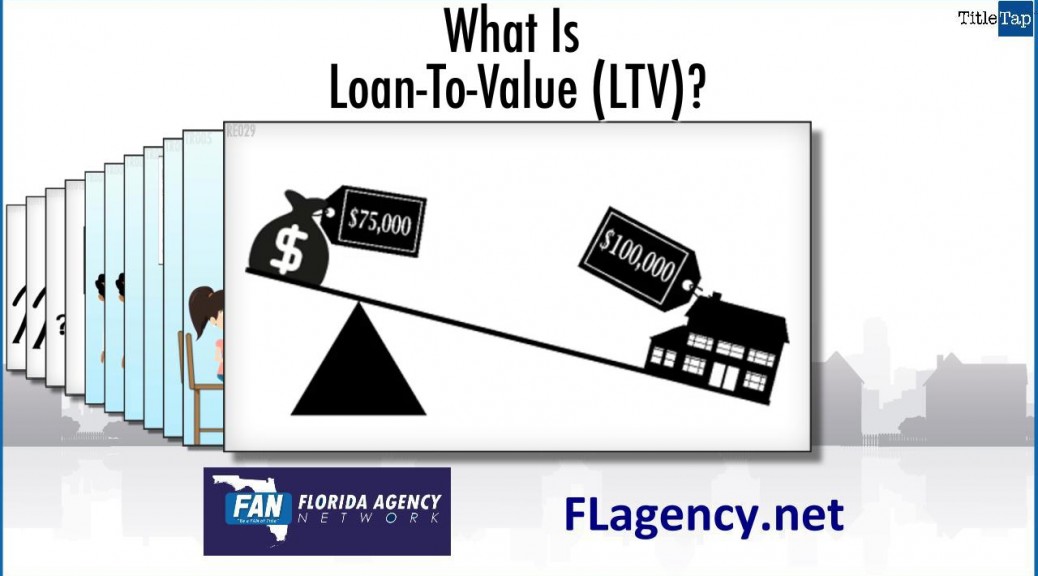
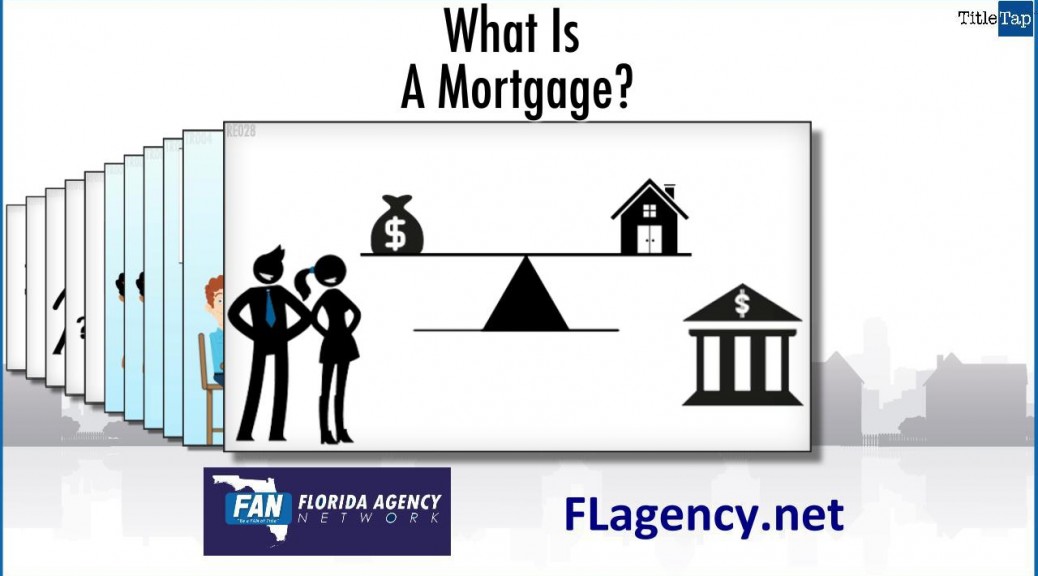
http://fwd5.wistia.com/medias/5zkry6bxx4?embedType=iframe&videoFoam=true&videoWidth=640
What are the “Ability to repay” rules about?
In a nutshell, as this video shows, new laws require lenders to make a good-faith assessment of a borrower’s capacity to pay back their loan over time.
It’s a longer-term view that goes beyond immediate income, debt and credit rating.
These new Federal laws- supervised by the CFPB – require lenders to ask more questions – about income, assets, employment, credit history, and monthly expenses – as they relate to the proposed loan.
For example, a lender offering a mortgage with a low initial rate must try to assess how a borrower will handle the later, higher rate as well.
If you’re applying to borrow ask whether the program you’re considering is a Qualified Mortgage
Ability-to-repay rules are built in to loans that meet Qualified Mortgage guidelines.